Data structures include arrays, linked lists, stacks, binary trees, and hash tables, among others
Data structures can help us store real world data (e.g. product categories), the method provided by abstracted class keep traverse and CRUD very handy.
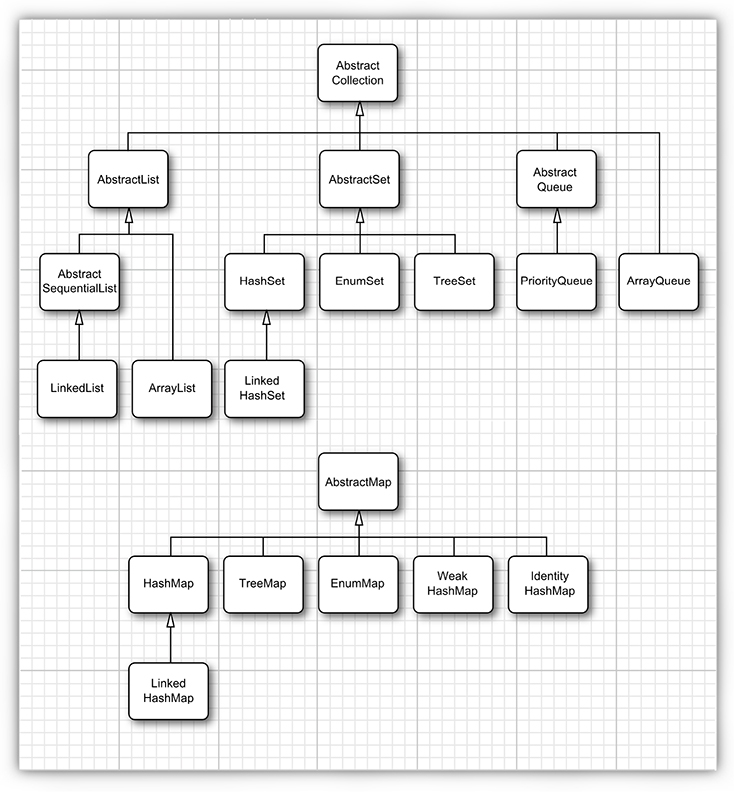
In my day-to-day programing, I found ArrayList, HashMap and HashSet is most useful.
ArrayList
ArrayList is the array can grow and shrink dynamically. To create an arrayList, we can use this code
// List.of (Java 9) will return non-sizeable, to make it modifiable, we need to pass the result into ArrayList constructor.
var categories1 = new ArrayList<>(List.of("table","chair","sofa","bed"))
// And here's another way to create array list:
List<String> categories2 = new ArrayList<String>();
categories2.add("table");
categories2.add("chair");
categories2.add("sofa");
categories2.add("bed");To iterate the array list, we can use the lambda expression (Java 8) to do that
categories1.forEach(c -> system.out.println(c));All the classes implement List interface are ordered collection. So the elements in ArrayList is also ordered, while the HashMap is not.
HashedMap HashMap is the key/value associations. As mentioned above, there’s no sequence guarantee for map.
var product = new HashMap<String, String>;
product.put("1234-567", "dinning table VANGSTA");
product.put("1234-568", "dinning table MELLTORP");
product.put("1234-569", "dinning table KULLABERG");
product.put("1234-570", "dinning table NORRÅKER");Set Set is the collection not allowing the duplication, it will make sure the item is unique in the set.
private static final Set<String> STATES = Sets.newHashSet("ACT", "NSW", "NT", "QLD", "SA", "TAS", "VIC", "WA");